Melanoma 101: Staging and Risk Factors
Melanoma 101: Staging
and Risk Factors
Knowing the risk factors and how melanoma is staged is vital
to understanding this type of cancer. When a physician determines the stage of
the cancer, often the staging determines the treatment, and how aggressive or
invasive the treatments might be. All the while, the physician will start
trying to reduce further risk of developing more melanomas. In this entry I
will go over the staging of melanoma and the risk factors.
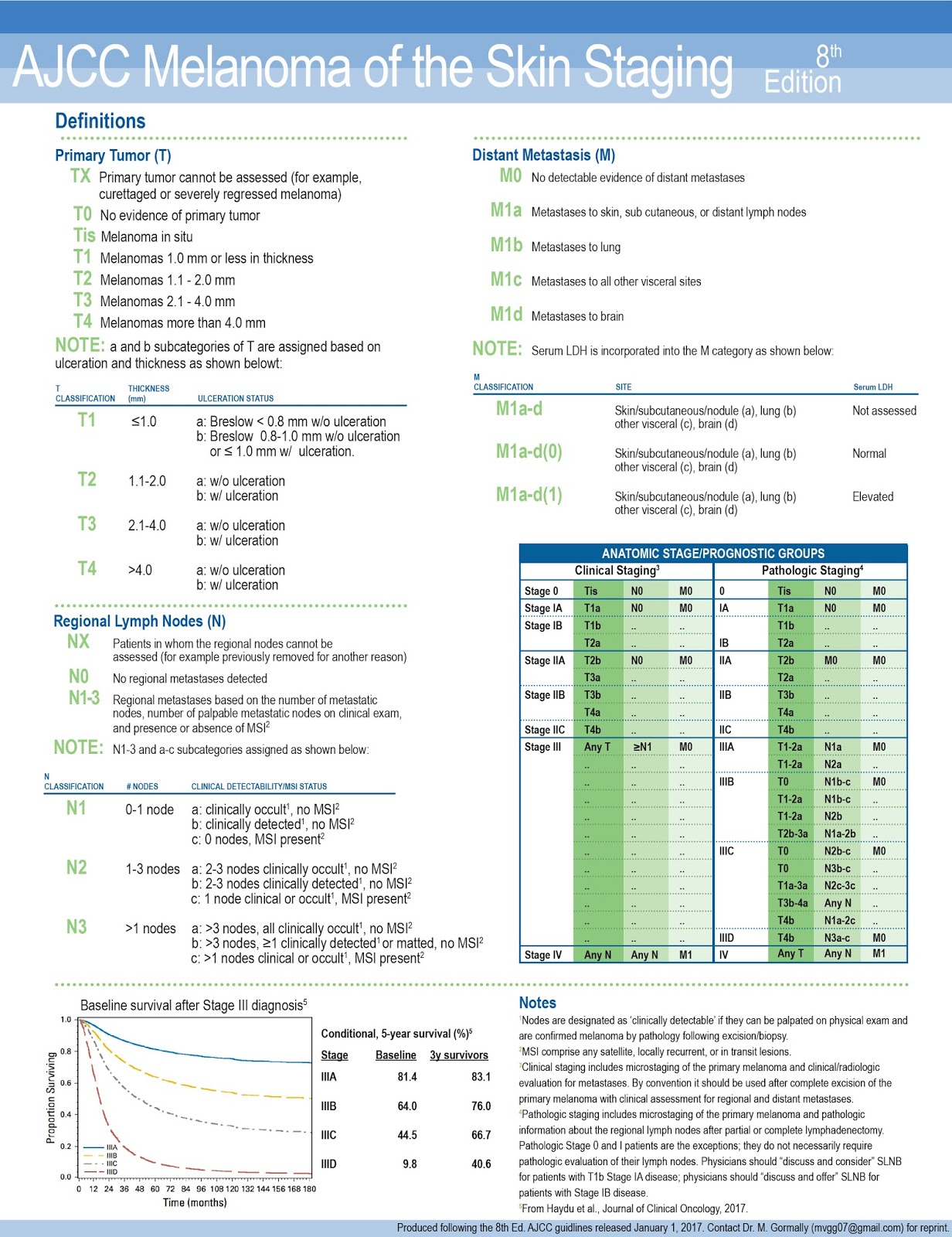
The staging system that is typically used with melanoma is
the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) system or known as TNM System.
The TNM system is based on three main pieces of information, T meaning tumor, N
meaning lymph nodes, and M meaning metastasis. The TNM system relies on those
three pieces of information where then a chart assigns a number I-IV, and if
applicable a letter. The T category is based on the assessment of the skin
lesion or tumor. The depth of the lesion and whether it is ulcerated matters. Melanoma
with a depth of less than one millimeter has little chance of spreading, while
the deeper the melanoma, the greater chance of spreading(metastasis).
Ulceration of the skin is important to note as well. Melanomas with ulcerations
tend to have a worse prognosis. The N category relates to if melanoma has
spread to the lymph nodes. The M category is regarding if the cancer has spread
to distant lymph nodes or to organs. The staging system is more definitive
following surgery from the tissue that was collected. The tissue that was
collected can then be measured post-surgery, allowing the proper depth of the
cancer to be determined and find out if it has spread to the surrounding lymph
vessels or organs. This scale can be used prior to surgery as a tool as well. (American
Cancer Society)
The TNM staging system is important in the understanding of the
cancer and helps gauge the severity of the cancer; risk factors are important
also. Risk factors play a role in aiding the physicians in providing a
diagnosis in certain types of melanomas. But more importantly, risk factors
need to be accessed to prevent re-occurrence.
The number of risk factors for melanoma can be, at times, difficult to
manage as the risk factors are as simple as living near the equator or having
one blistering sunburn during childhood. While some risk factors cannot be
helped, the risk factors that often make the difference in skin cancer is
rather preventable. These include but no limited to, exposure to UV light, tanning,
and failure to use sunscreen. For instance, use of tanning beds can increase
the chances of melanoma by one-point eight percent after each use. Limiting the amount of sun
expose has a direct correlation to the chances of developing melanoma and
sometimes that makes all the difference. (Inahl Infomation Systems)
Works Cited
American Cancer Society. "Melanoma Skin Cancer
Stages." (2017). https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/melanoma-skin-cancer-stages.html#references.
Inahl Infomation Systems. "Evidence Based Care
Sheet." Melanoma: Risk Factors and Pervention (2016). Document.

Comments
Post a Comment